Abrasive grit synthethic
CERADIA - Abrasive grit synthetic
| CNF | Abrasive grit for metal bond |
| CNF-E | Abrasive grit for galvanic bond |
| CMG | Abrasive grit coated |
| CRG | Abrasive grit for resin bond |
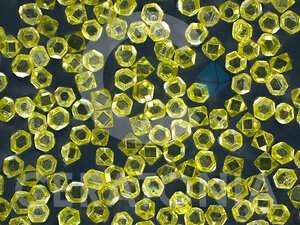
CERADIA CNF - Abrasive grit synthetic
CNF 3080
High-quality, crystalline abrasive grit with a small amount of inclusions. The crystal shape is little more irregular and due to the inclusions less thermally resistant. Good strength. Suitable for glass processing, décor grinding, facet grinding and drilling of crystal glass; metal grinding. Used in metal bond applications.
Grit sizes | CNF 3100 | CNF 3090 | CNF 3080 | CNF 3070 | CNF 3060 | CNF 3050 | CNF 3040 | ||
| Mesh | FEPA | ||||||||
| 80/100 | D 181 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| 100/120 | D 151 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 120/140 | D 126 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 140/170 | D 107 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 170/200 | D 91 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 200/230 | D 76 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| 230/270 | D 64 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| 270/325 | D 54 | X | X | X | |||||
| 325/400 | D 46 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
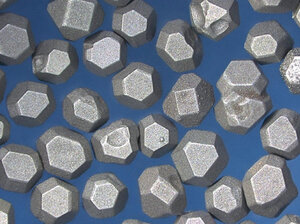
CMG 80
High-quality, crystalline abrasive grit with a small amount of inclusions. The crystal shape is little more irregular and due to the inclusions less thermally resistant. Good strength. Suitable for glass processing, décor grinding, facet grinding and drilling of crystal glass; metal grinding. Used in metal bond applications.
Grit size | CMG 100 | CMG 90 | CMG 80 | CMG 70 | CMG 60 | CMG 50 | CMG 40 | ||
| Mesh | FEPA | ||||||||
| 80/100 | D 181 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 100/120 | D 151 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 120/140 | D 126 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 140/170 | D 107 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 170/200 | D 91 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 200/230 | D 76 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 230/270 | D 64 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 270/325 | D 54 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| 325/400 | D 46 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
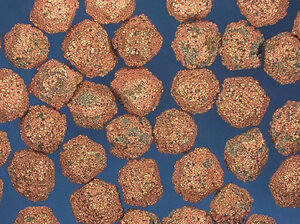
The coating can protect the diamond from erosion and at the same time expands the area of action of the diamond grit. This way the energy consumption is reduced and the cutting ability is increased.
Nickel
Nickel Ni 30 %, 50 %, 56 %
The coating can protect the diamond from erosion and at the same time expands the area of action of the diamond grit. This way the energy consumption is reduced and the cutting ability is increased. The surface of this kind of coating is smooth. The lifetime of the tools can be extended due to the extreme retention between the nickel layer and the surrounding bond.